
If the MAC address of C2 is present in its ARP cache table, it can then append the message with the corresponding MAC address and send it over the network (cable, switch). It first looks at its own ARP cache (which is a table that contains the IP addresses and their corresponding MAC addresses for computers/ systems within a network) to see if it already has the MAC address for the computer (C2), it wants to communicate with. So, when Computer (C1) gets the target IP address of the Computer (C2) it wants to communicate with, So, within a LAN segment computers identify each other and communicate with each other using the MAC Address. When it comes to the Layer 2 communications between networked systems, IP address is not used. What happens when one computer (C1) wants to communicate with another computer (C2) in a LAN segment? It is important to understand ARP to successfully troubleshoot a network. We will also discuss shortly about ARP poisoning and ARP broadcast storm. It has an interface with the network layer, which initiates the ARP request.In this article, let us first look at an example of what happens when two computers – CP1 & CP2 try to communicate with each other and through this example, understand what is ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) & ARP Cache Table and why they are required. This Means ARP works on the data link layer. 
ARP is the protocol that works as layer 2 of the OSI model. Each layer has an address for communication over the network. In computer networks, there are various layers of protocols. Only sends an ARP response back to the sending device with its own MAC address. But the device/computer whose IP address matches with the address in the ARP request. When the sending device needs to send a message, it broadcast the ARP request with the destination IP address. Now how the translation is done we will discuss. The router sends the response to the device to which the message needs to deliver.įrom the above example, it is clear what is the role of ARP in computer networks. From ARP, the router gets the physical address of the device.
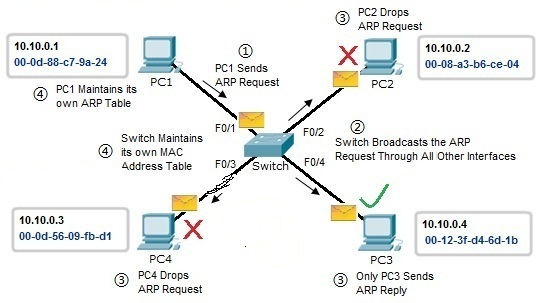
Upon response, the router knows the IP address of your LAN computer but does not know which physical device to send.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
